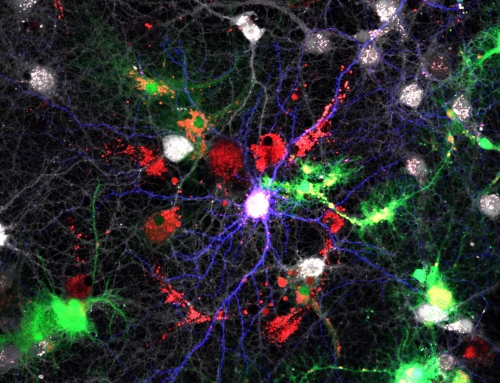
Visualizing the receiver structures of a nerve cell
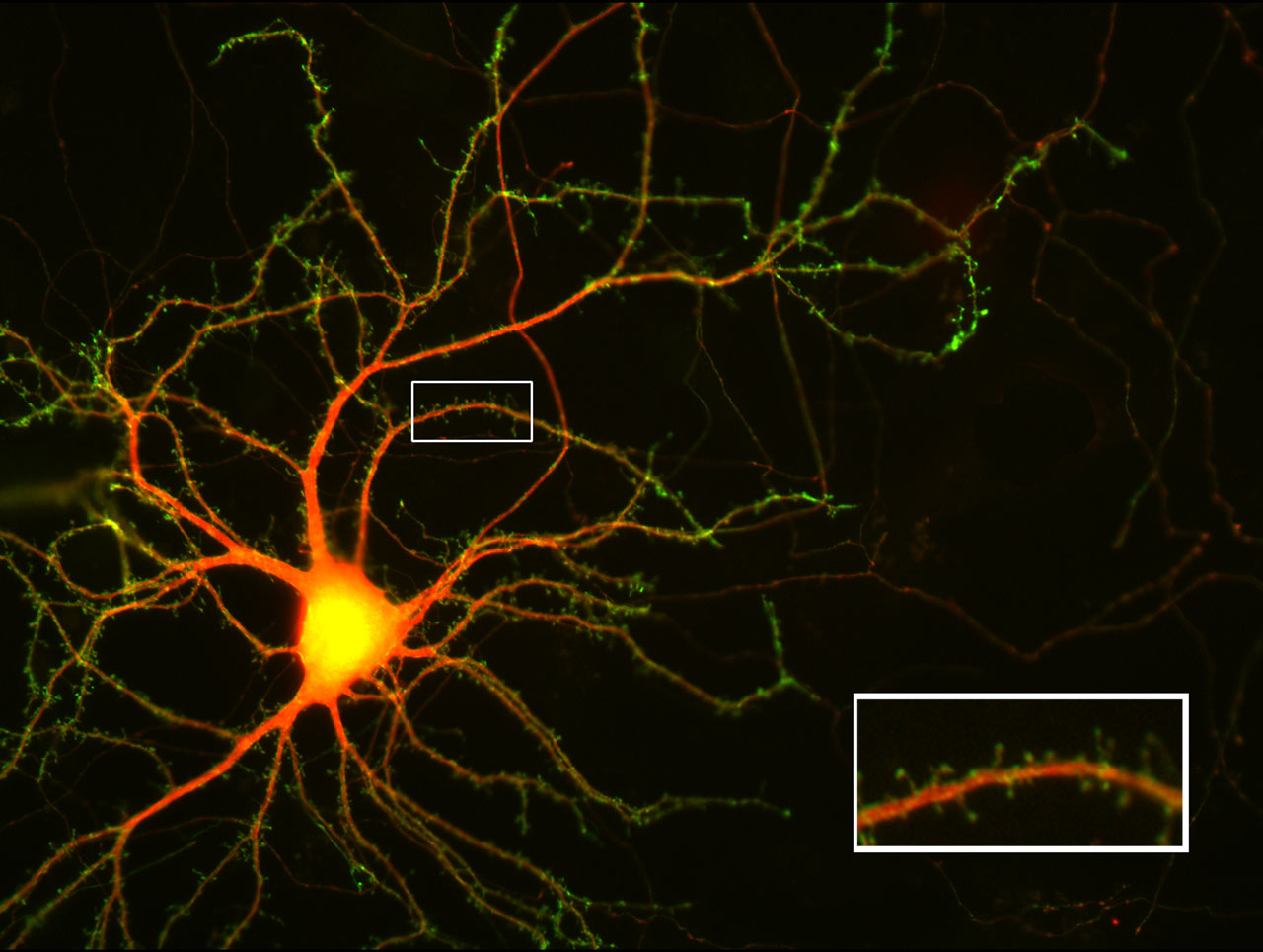
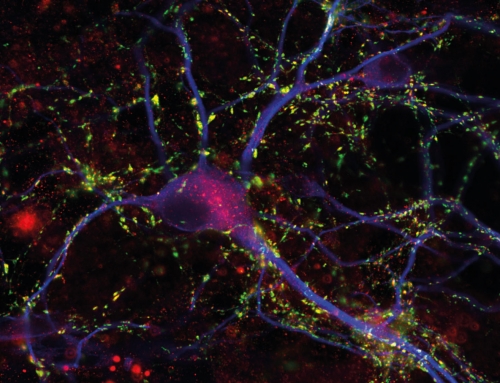
This cultured nerve cell was transfected, i.e. it was treated biochemically to take up DNA that is translated into protein by the cell. The first kind of DNA is from the disc anemone Discosoma and encodes a red fluorescent protein. This protein diffuses inside the nerve cell thus revealing the cell’s shape. The second kind of DNA is from the jelly fish Aquorea victoria and encodes a green fluorescent protein. We fused it to the molecule Neuroligin-1, which is enriched in the receiver sites (the postsynaptic apparatus) of nerve cells. The green fluorescent protein, attached to Neuroligin-1, reveals the shape, location and number of the reciever sites of the nerve cell.
Image details
Image acquisition technique: epifluorescence.
Courtesy T. Dresbach / UMG, CNMPB.